Description
BRANDS WE DEALS WITH
Matsubara, Yanmar, Hatlapa, Sperre, Hamworthy, Bitzer, J.P Sauer &Sohn Masch, Tanabe, Daikin, Carrier, Ishikawajima.
Types of Compressors
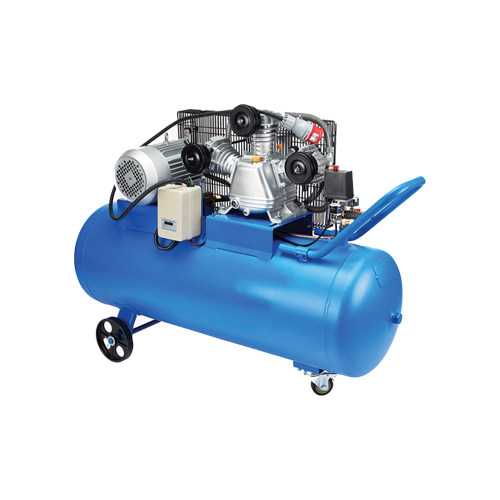
1. Reciprocating Compressors
- Function: Use pistons driven by a crankshaft to deliver gases at high pressure.
- Applications: Industrial plants, gas pipelines, refrigeration, air conditioning.
2. Rotary Screw Compressors
- Function: Use two meshing helical screws to compress the gas.
- Applications: Continuous operation in manufacturing, automotive, and other industries.
3. Centrifugal Compressors
- Function: Use a rotating impeller to add velocity to the gas and convert it to pressure.
- Applications: Large-scale industrial applications, HVAC systems, gas turbines.
4. Axial Compressors
- Function: Use a series of rotor and stator stages to progressively compress the gas.
- Applications: Aircraft engines, large industrial plants.
5. Scroll Compressors
- Function: Use two interleaved spiral scrolls to compress the gas.
- Applications: Air conditioning, refrigeration, and small-scale industrial applications.
6. Rotary Vane Compressors
- Function: Use a rotor with vanes that slide in and out to compress the gas.
- Applications: Medium-duty industrial applications, automotive industry.
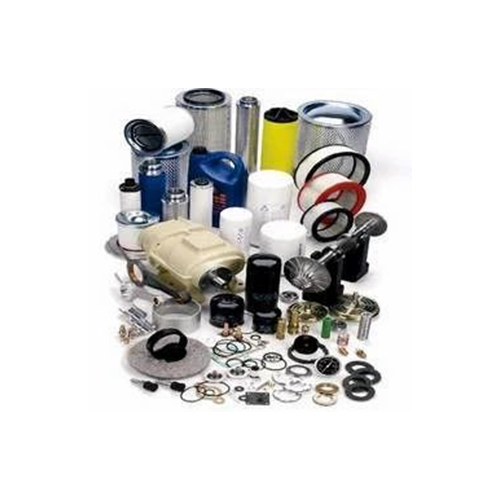
Common Spare Parts for Compressors
1. Reciprocating Compressors
- Pistons and Rings: Essential for the compression process.
- Crankshaft: Converts rotational motion into reciprocating motion.
- Valves: Control the intake and discharge of gas.
- Bearings: Support rotating parts and reduce friction.
- Gaskets and Seals: Prevent leaks and maintain pressure.
- Connecting Rods: Transfer motion from the crankshaft to the pistons.
- Cylinders: House the pistons and maintain the path for gas compression.
2. Rotary Screw Compressors
- Screw Elements: The main components that compress the gas.
- Bearings: Ensure smooth rotation of the screws.
- Seals: Prevent oil and air leaks.
- Oil Filters: Maintain the quality of lubrication oil.
- Coolers: Remove heat from the compressed air and oil.
- Gaskets: Ensure airtight assembly of components.
- Control Valves: Regulate the flow of air and oil within the system.
3. Centrifugal Compressors
- Impellers: Increase the velocity of the gas.
- Diffusers: Convert velocity into pressure.
- Bearings: Support the rotating shaft.
- Seals: Prevent leaks of gas and lubrication.
- Shafts: Transfer power to the impellers.
- Labyrinth Seals: Used to minimize gas leakage.
- Casings: House the internal components and withstand high pressures.
4. Axial Compressors
- Rotors and Stators: Primary components for gas compression.
- Blades: Attached to the rotors and stators to direct gas flow.
- Bearings: Support the rotating parts.
- Shafts: Transfer power through the compressor stages.
- Seals: Prevent leakage of gas.
- Vanes: Guide the gas flow within the compressor.
- Casings: Enclose the compressor stages and maintain structural integrity.
5. Scroll Compressors
- Fixed and Orbiting Scrolls: Compress the gas between them.
- Tip Seals: Maintain the seal between the scrolls.
- Bearings: Support the orbiting scroll.
- Motor: Drives the orbiting motion of the scroll.
- Crankshaft: Converts motor rotation to scroll movement.
- Shaft Seals: Prevent leaks around the crankshaft.
- Housing: Encases the scrolls and other components.
6. Rotary Vane Compressors
- Rotors: The main rotating component with slots for vanes.
- Vanes: Slide in and out to compress the gas.
- Bearings: Support the rotor.
- Seals: Prevent leakage.
- End Plates: Enclose the rotor and vane assembly.
- Oil Filters: Keep the lubrication oil clean.
- Springs: Assist in vane movement and ensure proper contact with the housing.
- Casings: House the internal components and ensure structural integrity.