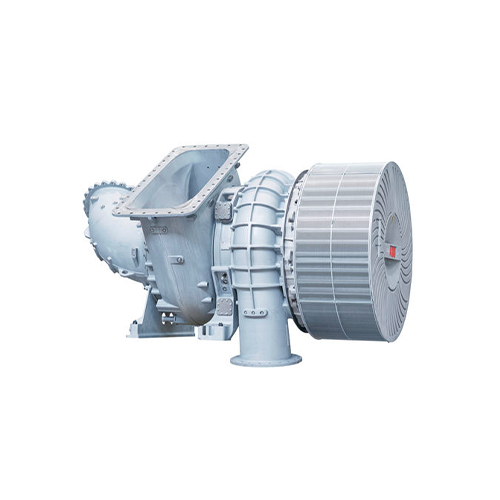
Description
Heat Exchangers
Types of Heat Exchangers:
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers:
- Function: Consist of a series of tubes, one set carrying the hot fluid and the other the cold fluid, allowing heat transfer between them.
- Applications: Power plants, oil refineries, chemical processes.
- Advantages: Durable, capable of handling high pressures and temperatures.
- Plate Heat Exchangers:
- Function: Use metal plates to transfer heat between two fluids. The fluids flow in alternate channels between the plates.
- Applications: HVAC systems, food and beverage processing, marine applications.
- Advantages: High efficiency, compact design, easy to clean.
- Air Cooled Heat Exchangers:
- Function: Use air to cool the fluid, often through finned tubes.
- Applications: Power plants, chemical industries, gas processing plants.
- Advantages: Do not require water, suitable for areas with limited water supply.
- Double Pipe Heat Exchangers:
- Function: Comprise two concentric pipes, one inside the other, where one fluid flows through the inner pipe and the other through the outer annular space.
- Applications: Smaller heat transfer requirements, high pressure applications.
- Advantages: Simple design, easy maintenance.
- Spiral Heat Exchangers:
- Function: Utilize spiral-shaped channels for the fluids, offering a compact and efficient design.
- Applications: Viscous fluids, slurries, and fouling applications.
- Advantages: High heat transfer efficiency, easy to clean.
- Plate and Frame Heat Exchangers:
- Function: Consist of a series of corrugated plates held together in a frame, allowing for flexible capacity adjustments.
- Applications: HVAC, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals.
- Advantages: High heat transfer rate, easy to expand or reduce capacity.
Spare Parts for Heat Exchangers
Common Spare Parts:
- Plates:
- Material: Typically stainless steel or titanium, chosen for their corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity.
- Function: Transfer heat between fluids, with corrugations to increase surface area and turbulence.
- Gaskets:
- Material: Made from rubber, nitrile, EPDM, or other elastomers.
- Function: Seal the plates to prevent leaks and direct fluid flow through alternate channels.
- Frame Components:
- Function: Support and hold the plates together, maintain pressure on the gaskets.
- Components: Fixed frame, movable frame, tie bars, and bolts.
- Nozzles:
- Function: Provide inlet and outlet connections for the fluids.
- Material: Typically made from the same material as the plates for compatibility.
- Seals and O-Rings:
- Function: Provide additional sealing, especially in high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
- End Plates:
- Function: Cap the ends of the plate stack in plate heat exchangers, ensuring fluid containment and pressure retention.
- Tie Bars and Bolts:
- Function: Hold the plate pack together and allow for tightening to maintain gasket compression.
- Flow Directors:
- Function: Ensure the correct flow paths and distribution of fluids through the plates.