Description
BRANDS WE DEALS WITH
BBC, Mitsubishi, KKB/ Holset, KKK, Napier, MAN B&W,ABB
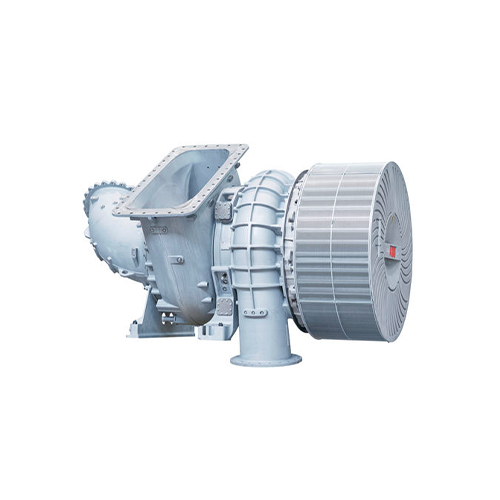
Turbochargers
Function and Benefits:
- Function: Turbochargers use exhaust gases from the engine to spin a turbine, which drives a compressor that forces additional air into the combustion chamber.
- Benefits: Increased engine power and efficiency, improved fuel economy, reduced emissions (when properly maintained).
Types of Turbochargers:
- Single-Turbo: Common in most applications, providing a significant boost in power.
- Twin-Turbo: Uses two turbochargers, either in parallel or sequentially, for smoother and broader power delivery.
- Variable Geometry Turbo (VGT): Adjusts the angle of the turbine blades to optimize performance across a range of speeds and loads.
- Twin-Scroll Turbo: Divides the exhaust pulses into two streams for improved turbine efficiency and reduced turbo lag.
- Electric Turbo: Uses an electric motor to spin the compressor, eliminating lag and providing immediate boost.
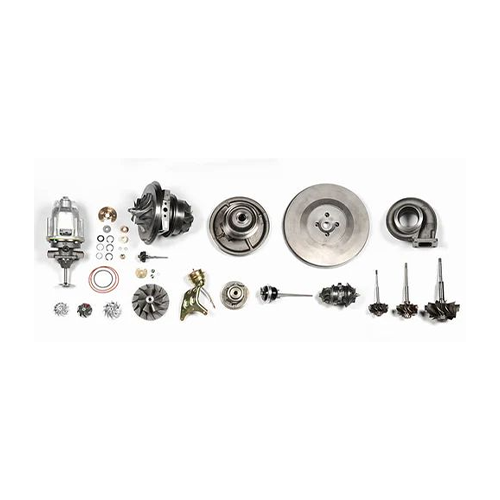
Common Spare Parts for Turbochargers
- Turbine Wheel and Shaft:
- Function: The turbine wheel is driven by exhaust gases, and the shaft transmits this motion to the compressor wheel.
- Material: Typically made of high-temperature resistant materials like Inconel.
- Compressor Wheel:
- Function: Compresses incoming air and forces it into the engine.
- Material: Often made from aluminum or titanium for strength and lightweight properties.
- Bearing Housing:
- Function: Houses the bearings that support the turbine and compressor shafts.
- Material: Usually made from cast iron or aluminum alloys.
- Bearings:
- Types: Journal bearings and ball bearings.
- Function: Reduce friction and support the rotating shaft.
- Oil Seals:
- Function: Prevent oil from leaking into the compressor and turbine housings.
- Material: High-temperature resistant rubber or metal.
- Turbine Housing:
- Function: Contains the turbine wheel and directs exhaust gases to it.
- Material: Made from cast iron or steel to withstand high temperatures.
- Compressor Housing:
- Function: Encases the compressor wheel and directs compressed air into the engine.
- Material: Typically aluminum.
- Actuators:
- Types: Wastegate actuators and variable geometry actuators.
- Function: Control the flow of exhaust gases to regulate the boost pressure.
- Gaskets and Seals:
- Function: Ensure airtight connections between different parts of the turbocharger.
- Material: High-temperature resistant materials like metal or composite.
- Intercoolers:
- Function: Cool the compressed air before it enters the engine, increasing its density and efficiency.
- Material: Typically made from aluminum for efficient heat transfer.