Description
Automation Systems
Types of Automation Systems:
- Integrated Automation Systems (IAS):
- Function: Monitor and control various ship systems, including propulsion, power generation, navigation, and safety.
- Features: Centralized control, real-time monitoring, alarms and alerts for system abnormalities.
- Power Management Systems (PMS):
- Function: Manage and optimize electrical power generation, distribution, and consumption on board.
- Features: Load shedding, peak shaving, blackout prevention, synchronization of generators.
- Engine Control Systems:
- Function: Control the operation of main engines, auxiliary engines, and propulsion systems.
- Features: Throttle control, speed and load monitoring, fault detection and diagnostics.
- Alarm and Monitoring Systems:
- Function: Monitor various parameters such as temperature, pressure, level, and vibration, and provide alarms for abnormal conditions.
- Features: Configurable alarms, trend logging, remote monitoring capabilities.
Electrical Units
Types of Electrical Units:
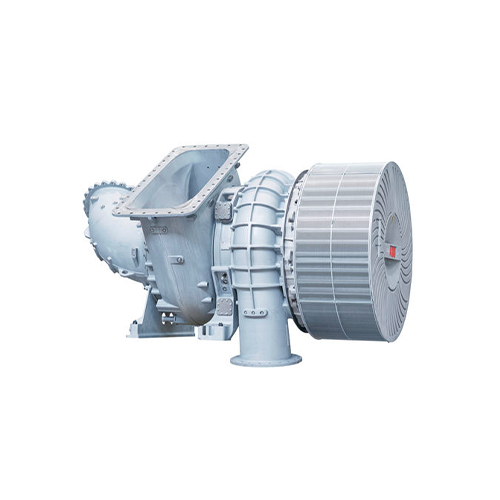
- Generators:
- Function: Convert mechanical energy into electrical energy to power ship systems and equipment.
- Types: Diesel generators, gas turbines, alternators.
- Features: Variable speed control, automatic voltage regulation, parallel operation.
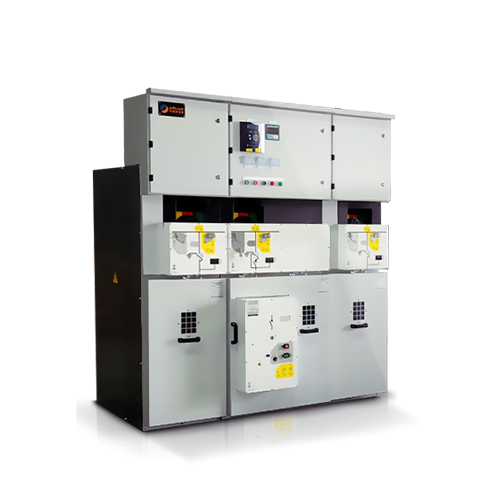
- Switchboards and Distribution Panels:
- Function: Distribute electrical power from generators to various consumers on board.
- Types: Main switchboards, distribution panels, control panels.
- Features: Circuit protection, metering, isolation and switching capability.
- Transformers:
- Function: Convert voltage levels for efficient power distribution and isolation.
- Types: Step-up transformers, step-down transformers, isolation transformers.
- Features: High efficiency, low noise, overload protection.
- Electrical Motors:
- Function: Convert electrical energy into mechanical energy to drive ship systems such as pumps, fans, and compressors.
- Types: Induction motors, synchronous motors, DC motors.
- Features: Variable speed control, overload protection, efficient operation.
- Battery Systems:
- Function: Provide backup power for critical systems, emergency lighting, and essential services.
- Types: Lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries, nickel-cadmium batteries.
- Features: High energy density, fast recharge capability, long service life.